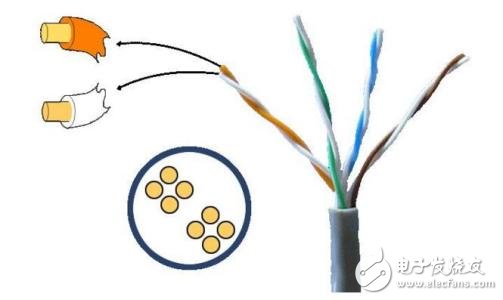
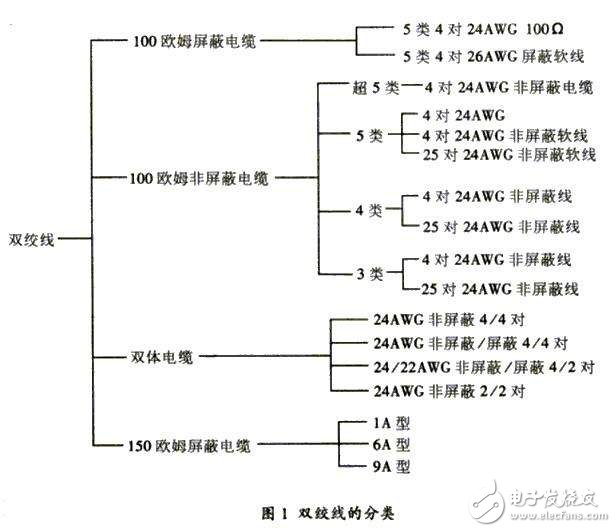
The English name for the twisted pair is Twist-Pair. It is the most commonly used transmission medium in integrated wiring engineering and consists of two copper wires with an insulating protective layer. The two insulated copper wires are twisted together at a certain density, and the electric wave radiated by each wire in the transmission is cancelled by the electric wave emitted from the other wire, thereby effectively reducing the degree of signal interference. The twisted pair cable uses a pair of mutually insulated metal wires to twist each other to resist some external electromagnetic interference. By twisting two insulated copper wires together at a certain density, the degree of signal interference can be reduced, and the electric wave radiated by each wire during transmission can be cancelled by the electric wave emitted from the other wire. The name "twisted pair" is also derived from this. The twisted pair cable is generally formed by two 22-26 insulated copper wires intertwined. In actual use, the twisted pair cable is wrapped in an insulated cable sleeve by a plurality of pairs of twisted pairs. Typical twisted pairs have four pairs, and more pairs of twisted pairs are placed in a cable jacket. This is what we call twisted pair cable. In a twisted pair cable (also called a twisted pair cable), different pairs have different twist lengths. Generally speaking, the twist length is within 38.1 cm to 14 cm and is twisted counterclockwise. The twist length of the adjacent pair is above 12.7cm. The denser the twisted wire is, the stronger the anti-interference ability is. Compared with other transmission media, the twisted pair is in terms of transmission distance, channel width and data transmission speed. Subject to certain restrictions, but the price is relatively low. The following is a brief introduction to the classification of twisted pairs. Twisted pair common types are Category 3, Category 5 and Category 5, and the latest Category 6 line. The former has a thin wire diameter and the latter has a thick wire diameter. The models are as follows: 1) Category 1 line: mainly used for voice transmission (a type of standard is mainly used for telephone cables before the early 1980s), which is different from data transmission. 2) Class 2 line: The transmission frequency is 1 MHz, which is used for voice transmission and data transmission with a maximum transmission rate of 4 Mbps. It is commonly used in the old token network using the 4 MBPS specification token transfer protocol. 3) Category 3: Refers to the cable currently specified in the ANSI and EIA/TIA568 standards. The cable has a transmission frequency of 16 MHz and is used for voice transmission and data transmission with a maximum transmission rate of 10 Mbps is mainly used for 10BASE-T. 4) Category 4 cable: This type of cable has a transmission frequency of 20 MHz. The data transmission for voice transmission and the maximum transmission rate of 16 Mbps is mainly used for token-based LAN and 10BASE-T/100BASE-T. 5) Category 5 cable: This type of cable increases the winding density, jacket is a high quality insulation material, transmission rate is 100MHz, used for voice transmission and data transmission with a maximum transmission rate of 10Mbps, mainly used for 100BASE-T and 10BASE-T network. This is the most commonly used Ethernet cables. 6) Super Category 5: Super Category 5 has low attenuation, low crosstalk, and higher attenuation and crosstalk ratio (ACR) and signal-to-noise ratio (StructuralReturnLoss), smaller delay error, and greatly improved performance. . The Super Category 5 cable is mainly used for Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Mbps). 7) Category 6 cable: The transmission frequency of this type of cable is 1MHz ~ 250MHz. The Category 6 wiring system should have a large margin in the integrated attenuation crosstalk ratio (PS-ACR) at 200MHz. It provides 2 times the Category 5 super Category. bandwidth. The transmission performance of Category 6 cabling is much higher than the Category 5 standard and is best suited for applications with transmission rates above 1Gbps. An important difference between Category 6 and Category 5 is that it improves performance in terms of crosstalk and return loss. For a new generation of full-duplex high-speed network applications, excellent return loss performance is extremely important. The basic link model is eliminated in the six categories of standards. The cabling standard adopts a star topology. The required cabling distance is: the length of the permanent link cannot exceed 90 m, and the channel length cannot exceed 100 m. 8) Super Category 6 or 6A (CAT6A): The transmission bandwidth of such products is between Category 6 and Class 7, with a transmission frequency of 500 MHz, a transmission speed of 10 Gbps, and a standard outside diameter of 6 mm. Like the seven categories of products, the country has not yet issued formal testing standards, but there are such products in the industry, and each manufacturer announces a test value. 9) Category 7 line (CAT7): The transmission frequency is 600MHz, the transmission speed is 10Gbps, the single-wire standard outer diameter is 8mm, and the multi-core standard outer diameter is 6mm. The larger the type number and the newer the version, the more advanced the technology and the wider the bandwidth, and of course the more expensive the price. These different types of twisted pair marking methods are specified as follows. If it is a standard type, it is marked by CATx. For the commonly used Category 5 and Category 6 lines, the online skin is marked as CAT5 and CAT6. If it is an improved version, it will be marked by xe. For example, if the super five lines are marked as 5e (the letters are lowercase instead of uppercase). According to the presence or absence of shielding layer, the twisted pair is divided into Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) and Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP). The shielded twisted pair has a metal shield between the twisted pair and the outer insulating envelope. Shielded twisted pair is divided into STP and FTP (FoilTwisted-Pair). STP means that each line has its own shielding layer, and FTP only works when the entire cable has shielding and both ends are properly grounded. Therefore, the entire system is required to be a shielding device, including cables, information points, crystal heads and patch panels, and the building needs to have a good grounding system. The shielding layer can reduce radiation, prevent information from being eavesdropped, and prevent external electromagnetic interference from entering, so that the shielded twisted pair has a higher transmission rate than the similar unshielded twisted pair. Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) is a data transmission line consisting of four pairs of different color transmission lines, widely used in Ethernet and telephone lines. Unshielded twisted pair cables have the following advantages: 1. Unshielded jacket with small diameter, saving space occupied and low cost; 2, light weight, easy to bend, easy to install; 3. Minimize crosstalk or eliminate it; 4, with flame retardancy; 5, with independence and flexibility, suitable for structured integrated wiring. Therefore, unshielded twisted pair is widely used in integrated wiring systems. In these two categories, it is divided into 100 ohm cable, double body cable, large logarithmic cable, 150 ohm shielded cable and so on. Regardless of the type of line, the attenuation increases with increasing frequency. When designing the wiring, it is important to consider that the attenuated signal should also have a large enough amplitude to be correctly detected at the receiving end under noisy interference. The ability of a twisted pair to transmit multiple high rate (Mb/s) data is also strongly related to the encoding method of the digital signal.
Problems with failing factory relays, connectors/terminals and fuse contacts are also common when excessive load is placed on them.
Yacenter
has experienced QC to check the products in each process, from developing
samples to bulk, to make sure the best quality of goods. Timely communication
with customers is so important during our cooperation.
If you can't find the exact product you
need in
the pictures,please don't go away.Just contact me freely or send your sample
and drawing to us.We will reply you as soon as possible.
Plate Harness,Pcb Board Harness,Pcb Board Wiring Harness,Pcb Plate Harness Dongguan YAC Electric Co,. LTD. , https://www.yacentercn.com