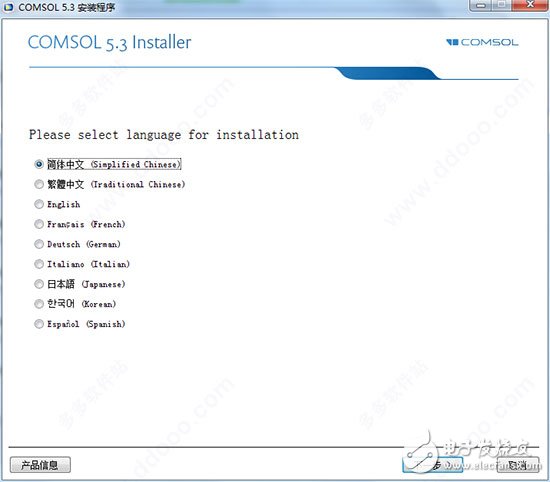
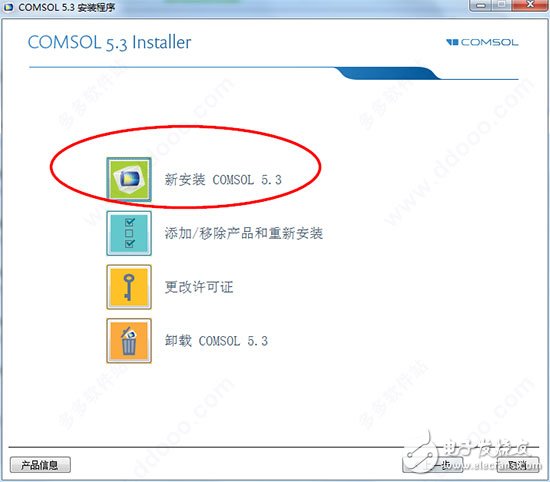
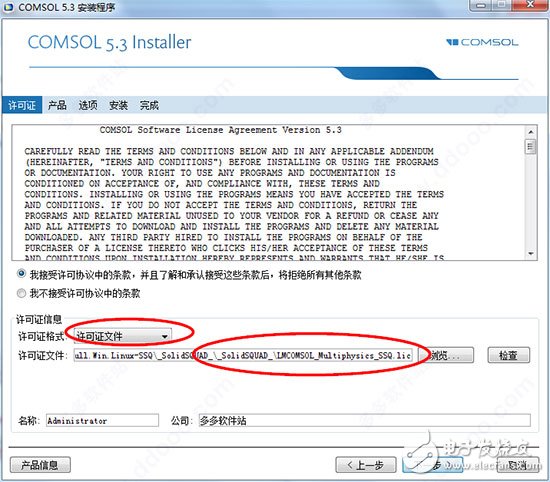
The performance of COMSOL Multiphysics version 5.3 has been greatly improved compared to versions 5.2a and lower. When we deal with models made up of thousands of domains, boundaries, edges, or points, we can more fully appreciate the superior performance of the new version. The COM5.3 software version 5.3 can be said to bring significant performance improvements. The performance of COMSOL Multiphysics version 5.3 has been greatly improved, the response speed has been increased tenfold, and several functions have been added and improved for functions such as solving, meshing, and physics-based plug-in modules. By using version 5.3, you can create models more efficiently, as well as deploy and run apps. Below we will detail the comsol 5.3 version highlights, comsol5.3 crack installation, comsol5.3 installation tutorial. Features of comsol 5.3: 1. Solve multi-field problems—solve equations. Users can easily implement multi-physics direct coupling analysis by simply selecting or customizing different combinations of partial differential equations. 2, completely open architecture, users can easily define the required professional partial differential equations in the graphical interface. 3. Solving parameters controlled by arbitrary independent functions, material properties, boundary conditions, and loads all support parameter control. 4, professional computing model library, built-in a variety of commonly used physical models, users can easily select and make the necessary modifications. 5, embedded in the rich CAD modeling tools, users can directly 2D and 3D modeling in the software. 6. Comprehensive third-party CAD import function to support the import of current mainstream CAD software format files. 7, powerful meshing ability, support a variety of meshing, support mobile grid function. 8, large-scale computing capabilities, with 64-bit processing power and parallel computing capabilities under Linux, Unix and Windows systems. 9, rich post-processing functions, can output and analyze various data, curves, pictures and animations according to user needs. 10, professional online help documentation, users can easily grasp the operation and application of the software through the operating manual of the software. 11, multi-language operation interface, easy to learn and use, convenient and fast load conditions, boundary conditions, solution parameter setting interface. Highlights of the comsol 5.3 release also include: 1, general update · Use the new model method features in the Model Builder to automate and control a large number of modeling tasks · Custom actions can be performed when you click a drawing in the Graphics form object in the app · Manage cluster settings and usage log files in COMSOL Server products · Automatic generation of pyramid unit transition layers between hexahedron, prism and tetrahedral mesh Automatically remove fine geometric details to create a more stable mesh · Simultaneously generate visual effects of different scale values ​​on different y-axis of one-dimensional drawing · Generate visual effects of specific and important 3D drawing parts based on selected filters · Direct and iterative solver recommendations from the receiving system, whether you choose to solve quickly or save memory · Combine two transient or parametric solutions for future use · Generate adaptive meshes that integrate with user-defined grid sequences 2, electromagnetics · Simulate electrostatic applications using a new physics interface based on the boundary element method, which can also be used in conjunction with finite element modeling methods · Perform fast capacitance and general block matrix calculations using new research types ·View and operate the new permanent magnet motor teaching model · Use the new "parts library" for standard RF and microwave components · Apply automatic termination of ray in ray optics models with user-defined border or intensity reduction · Import photometric data files for ray optical modeling · Use the new Schrödinger equation interface for 1D, 2D and 3D quantum mechanical calculations 3. Structural mechanics and acoustics · Easier to develop models with self-balancing loads with the automatic restraint of rigid body motion · Quickly evaluate the elastoplastic analysis requirements of components by calculating the safety factor in line elasticity analysis · Perform stress linearization calculation on pressure vessels · Use the new Lemaitre-Chaboche viscoplastic material model · View and operate the new "Rotor Bearing System Simulator" App for rotor dynamics studies · View and further use two new teaching models: vibration and noise coupling in gearbox and induction motors · Apply a perfect matching layer (PML) to absorb the outgoing wave in transient pressure acoustic analysis · Analysis of transient hot viscous acoustic applications 4, fluid flow and heat transfer · Study fluid flow using the new highly automated and stable Algebraic Multigrid (AMG) solver · Applying a new vf turbulence model with strong turbulence anisotropy for CFD simulation · Use automatic processing of near-wall flow to switch between different formulas when simulating turbulence associated with grid resolution · Simulate well systems using new boundary conditions that can easily define injection inflows and outflows · Develop an air heat and moisture transfer model using the new physics interface · Use material attribute data in the building and refrigeration materials library · scatter and direct solar radiation in the surface-to-surface radiation model Reduce the cost of calculation by simulating thermal radiation in all directions simultaneously using multiple symmetry planes 5. Chemistry • Application modeling for enhanced reaction using multi-physics interfaces for porous media reaction flows and transfers, as well as cracks in impervious media and porous media Expand the modeling capabilities by using the charge-conserved Nernst-Planck and Poisson equations provided in the new interface · Simulate acid-base balance in water systems using the new "electrophoretic transport" interface · Introducing Tangnan balance in the updated interface for ion exchange membranes and thin electrolyte layers ·Using boundary element method to simulate current distribution on large, complex and thin structures · Use of new current distribution, thin liquid layer enhanced corrosion modeling function in the shell interface 6, multi-function and interface • Apply periodic conditions for particle tracking in periodic structures or geometries with sector symmetry · Easily simulate particles in rotating machinery with the new rotating coordinate system function · Supports the rapid and easy release of particles at random initial positions · Efficiently synchronize CAD assembly selection with LiveLink for SOLIDWORKS and LiveLink for Inventor Support for synchronizing these entities with LiveLink for AutoCAD in simulations using curves and points · A new tutorial on how to import PCB geometry models from ODB++ archive files and perform meshing 7, COMSOL Multiphysics · Improved responsiveness to online context-sensitive help. · Fixed a character encoding error on the Simplified Chinese technical support page. · Fixed an issue of unnecessary mesh rebuilds when opening old models; this problem only affects models that use mesh parts under globally defined nodes. · Fixed an issue with importing meshes into geometry nodes in the model tree or re-slicing meshes for "deformation geometry". Isolated edges and vertices in geometry could cause geometric damage, making COMSOL Multiphysics software stable. Two new built-in methods for returning information associated with model tree view nodes in the API; the view.geom() method returns geometric sequences or null values ​​for geometry-independent views, and the view.getSDim() method Returns the spatial dimension. • Change the default constraint method for periodic conditions from cell type to node; this change makes the default constraint method consistent with the previous version. · Improved terminology in the Spanish and French COMSOL Desktop user interfaces. · Improved performance of the initial solution while improving other performance. · Added an error message to display when the geometry optics or ray-acoustic interface selection contains un-segmented mesh fields; typically, the choice of these two physics interfaces should not include un-segmented meshes and Empty area. · Fixed an issue that prevented the opening of MPH files stored on Samba disks when running on macOS operating system software. · Added a new feature that makes iterative solver recommendations now available for acoustic-structural interactions in the time domain. · Fixed an issue with accessing locally installed help files when running COMSOL Multiphysics connected to a remote COMSOL Multiphysics server session. • Improved performance of certain variables used in multiple interfaces based on boundary element methods within component coupling operators. · Fixed an issue with the COMSOL Multiphysics server, which now works fine on Linux clusters. • Predefined iterative solver recommendations can now be used in the time domain of the acoustic-piezoelectric interaction model. · Improved stability of Case Library Updates in a number of ways, including instant integration of added or modified model documents. · Fixed App layout issues and corrected errors that might be triggered by undefined variables. · Fixed an issue with the use of a stable convection-diffusion equation interface with a unit system set to none. The COMSOL Multiphysics "case library" based on the KdV equation and the soliton model in the equations folder has been improved with better temporal resolution. · Corrected an error that caused the SCGS smoother containing Vanka variables to not work properly in cluster simulation. · Fixed an issue that occurred when saving MPH files that were temporarily locked by other programs, such as Google Drive Online Storage Service or File Sync software such as Dropbox Storage. 8, COMSOL Server · Fixed multiple stability issues. 9, AC / DC module · Improved performance of some demo apps in the Case Library. • Improved performance of certain variables used in multiple interfaces based on boundary element methods within component coupling operators. 10, acoustic module • Corrected the time-domain PML formula for pressure acoustics to eliminate unwanted reflections from two-dimensional axisymmetric models. · Improved dynamic help for the "acoustic module". • Fixed an error in the compression factor expression in the porous media acoustics Johnson-Champoux-Allard-Lafarge option. 11, App Developer · Fixed an issue with running external class nodes through batch jobs. 12, CAD import module Fixed an issue with performing feature removal and repair operations, which was previously prompted with the error message "Error when serializing reference to: GeomObject" when trying to run the study again. · Fixed an issue with File Import for CATIA V5 products, which was previously incorrectly imported with some CATIA V5 files in the 5.3 version. 13, CFD module • Updated the two-phase flow multiphysics coupling node in the model tree to always display the temperature input box. 14. Chemical Reaction Engineering Module • Updated step-by-step modeling operation instructions for the “zone electrophoresis†model. 15, ECAD module · Fixed an issue where some text objects were not automatically identified and ignored when importing ODB++ files. · Fixed an issue with importing GDS files containing mirrored arrays. 16, electroplating module Improved step-by-step modeling operation instructions for the "Spinning Cylindrical Hull Battery" model. 17. Geotechnical Mechanics Module · Fixed an error in the isotropic hardening option, which was used in previous versions with an elliptical end cap in the soil plastic material model. 18, heat transfer module • Corrected expressions for post-processing variables nteflux and nteeflux in a model based on the thermoelectric effect interface. • Thermal expansion is enabled in models that contain isothermal domains. · Fixed an issue with defining variables Td and Tu on the boundary, which was seen in some configurations used in the combination of the isothermal domain interface and the thin layer. • Improved equation display for the wet air version of the moisture delivery interface. · Fixed a legend that reversed on the natural convection sketch. • Fixed the definition of the energy balance post-processing variables for models with diffuse surface boundary conditions on the inner boundary. · Fixed an issue with missing entities in the selection loaded from the assembly component. 19. LiveLink for Inventor · Fixed an issue where the selection sometimes failed after adding a feature node to a window interface of the Model Builder. 20, LiveLink for MATLAB · Fixed an issue with using mphstart and mphlaunch when the installation path for COMSOL Multiphysics contains spaces. Fixed an issue with mphnavigator when selecting a parameter node in the model tree while clicking on "Replication Set". 21. Nonlinear structural mechanics module · Fixed a cycle-dependent error that occurred when viscoelasticity was combined with user-defined hyperelastic materials. · Corrected an error in the Navarro-Herring creep model that might not define a variable name. 22, plasma module · Fixed an undefined error in variables that might occur when using symmetric boundary conditions in heavy matter interfaces. • On the boundary of the heavy mass transfer interface where the normal velocity is not zero, the correct weak contribution is added for the “flux†condition. 23, ray optics module · Corrected the description of the coupled gopminop of the component that previously contained the error. · Fixed an issue with the features of the illuminated surface, which can now be initialized in a two-dimensional axisymmetric model. • Fixed an issue with the entry features of geometric optics interfaces, which can now be initialized in a two-dimensional axisymmetric model. 24, structural mechanics module • Corrected a symbolic error in the strain variable calculated in the spring base node in some cases. • Updated the heat source item in the thermoelastic interface so that it is now zero only when the structural transient behavior is set to contain inertia terms. · Corrected an error that the point quality condition could not be used in the 2D version of the beam interface; this error was previously seen when the study attribute was enabled to contain geometric nonlinearities. Fixed an error on the external stress node of the shell interface. If the global coordinate system option was previously selected and other coordinate systems were used in the shell local coordinate system node of the model tree, the stress added to the node would become Incorrect. • Fixed an issue where the calculated torque was incorrect. This problem occurred when the calculated reaction force was selected for the rigid connection line in the solid mechanics interface; the result was previously scaled by the boundary area of ​​the attached rigid connection line. Fixed an issue where the variable or expression could not be used in the input box of the cross section in the beam interface. · Fixed an issue where too many constraints were generated when the Solid Mechanics interface was used in conjunction with the "Optimization Module" interface in some cases. · Corrected errors that could not incorporate external stress relationships and contact features. · Fixed an issue with exporting beam section properties. • Fixed a problem when the 2D model contained multiple rigid link features with inertial mass and moment of inertia properties. 1. Select language, support (Simplified Chinese) 2. Click on "New Install COMSOL 5.3" 3. Allow the user agreement, change the license format to "License File", and then click Browse to load "LMCOMSOL_Multiphysics_SSQ.lic" under the "_SolidSQUAD_" directory in the installation package. 4, choose to install the module and the installation directory 5, here you can add links to MATLAB, Pro / E and other software. 6, waiting for the installation to complete 7. We installed the certificate when we installed it, so we can start the experience by running the shortcut of the desktop COMSOL 5.3 crack version. Led Neon Flex ,Neon Flex Adalah,Flexible Led Neon Strip Lights,Led Neon Tube Lights NINGBO SENTU ART AND CRAFT CO.,LTD. , https://www.lightworld-sentu.com
COMSOL Multiphysics 5.3 integrates eight modules including structural mechanics module, chemical engineering module and heat transfer module. It contains more than 30 additional modules for you to choose from, with unparalleled simulation and simulation capabilities. COMSOL can extend the modeling capabilities by linking COMSOL Multiphysics simulation to a variety of software types such as engineering calculations, CAD and ECAD through specialized physical interfaces and tools in the fields of electrical, mechanical, fluid flow and chemistry. Simulating challenging industrial applications in the electromagnetic, mechanical, fluid, and chemical industries. 
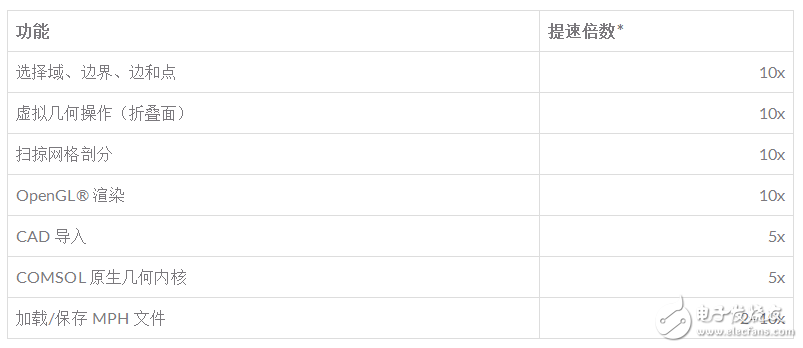
The table below shows the most important performance improvements and the estimated speed multipliers when working with large models.