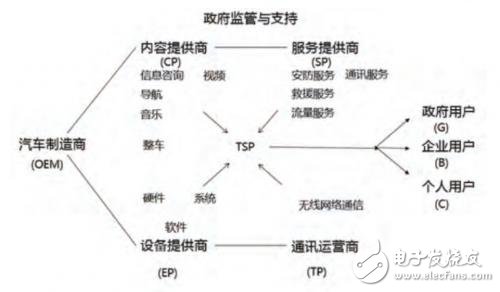
The Internet of Vehicles is a typical application of the Internet of Things technology in the field of transportation. As the market matures, its connotation is further expanded. This article discusses the narrowly defined vehicle network, TeleemaTIcs service (in-vehicle information service system), which refers to the service system that integrates users with various service resources through the vehicle terminal. Through the combing and analysis of several development models of the existing vehicle networking, the article attempts to find a correct development path for the future of the vehicle network. Since 2015, Premier Li Keqiang proposed in the government report that "the Internet +" action plan will be formulated to promote the integration of mobile Internet, cloud computing, big data, and the Internet of Things with modern manufacturing, and promote the healthy development of e-commerce, industrial Internet and Internet finance. After the strategy of guiding Internet companies to expand the international market, the Internet has become a trend of subversion and transformation of traditional industries. The Internet is not only re-exploring the potential of the industry, but also re-engineering and subverting traditional industries with Internet thinking. . From Tesla redefining people's understanding of the car, to Apple, Google, Microsoft, Ali, Baidu, LeTV and other Internet giants to fully engage in the battle for automotive Internet, the era of car networking has arrived. The narrowly defined Internet of Vehicles, the TelemaTIcs service (in-vehicle information service system), refers to a service system that integrates users with various service resources through the vehicle terminal. The broad-based car network also includes intelligent transportation systems. 1.1 Status of the development of vehicle networking The connotation of the Internet of Vehicles has evolved from the earliest stage of navigation to the initial stage of TSP service, and then to the intermediate stage of "scenario" service. The “Scene†service is designed for drivers, passengers, OEMs and vehicle managers to form a comprehensive service system that integrates multi-role and multi-scene applications, as shown in Table 1. Table 1 Evolution of the application scenario of the Internet of Vehicles 1.2 The future of vehicle networking applications From the perspective of the final end of the Internet of Vehicles, it is the realization of driverlessness, which is the core part of intelligent transportation. The Internet of Vehicles is the core information communication platform of the future ITS (Intelligent Transportation System), playing more and more roles [1]. (1) Safe driving of roads The Internet of Vehicles can effectively reduce the incidence of traffic accidents through emergency braking, accident site warning, crossroad warning, speed warning, retrograde warning, and prohibition of fatigue driving, making travel safer. (2) Prevent traffic jams The vehicle network can realize road condition monitoring, early warning, non-stop billing, etc. to effectively alleviate traffic congestion pressure, reduce traffic congestion by about 60%, provide road utilization rate, and improve existing road capacity by 2 to 3 times. , shorten the travel time. At the same time, it can reduce energy consumption and reduce vehicle exhaust emissions by 25% to 30% [2]. (3) Promote the upgrading of the automobile industry Implement the vehicle networking strategy, incorporate the automobile manufacturing industry into the innovation environment of China's new communication technology, enhance the new technology capabilities of automobiles, and drive the development and upgrading of the automotive industry with digital technology. (4) Realizing intelligent transportation All major parts of traffic management can be realized through the Internet of Vehicles, such as traffic signal intelligent control, traffic accident handling, intelligent parking lot management, electronic non-stop charging, bus intelligent dispatching, etc., to realize intelligent transportation with vehicle networking as communication management platform. . The structure of China's car networking industry is complex, as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 Sketch of the car network industry chain (1) OEM (OEM) The OEM is the carrier of the realization of the Internet of Vehicles service. It is at the center of the traditional industrial chain, has a large voice and appeal, can effectively integrate many resources, and has great advantages in the development of the Internet of Vehicles. However, due to the competitive relationship between the various car manufacturers, the car networking services provided by the OEMs are limited to their own brands, making the car networking services of each brand independent and incompatible, and the car network services provided by various OEMs are generally higher. Can only be bundled and installed on their own brand cars, the scope of customers is limited, and the aftermarket is unfavorable. (2) Content Provider (CP) The content provider mainly provides music content, video content, news content, weather content, etc., which is embodied in the form of direct content access, car APP, etc., and the discourse power in the entire car networking industry is weak. (3) Service Provider (SP) Service providers mainly provide security services, rescue services, call center services, insurance services, etc. Most service providers cooperate with other companies (such as OEMs, communication companies, etc.) to transform into TSP. (4) Vehicle Information Service Provider (TSP) The vehicle information service provider directly faces the user in the industry chain, providing users with navigation, road information remote diagnosis and control, entertainment information, dealer activities and other services. TSP is at the core of the entire industry chain, integrating and regulating service content forward, and there are two ways to provide services in the future: One is as a “white card†service provider, which is determined by the OEM; The other is to provide the TelemaTIcs service to users by TSP's own brand. In addition to integrating resources and providing services, TSP also undertakes the task of collecting fees and distributing profits [3]. (5) Equipment Provider (EP) The equipment provider provides in-vehicle terminal equipment including hardware, system, software and application integration. In the pre-installation market, TIer 1 is used as a supporting vehicle for the OEM. According to the design scheme provided by the OEM, the relevant system software and positioning software will be provided. It is integrated with electronic components such as sensor chips and GPS modules to produce dedicated vehicle terminals. In the aftermarket, simply buy equipment or cooperate with service providers to provide TSP services. In general, the right to speak is not high. (6) Communication provider (TP) Communication providers provide wireless network communication services, including network services and telephone services. They are the infrastructure for the implementation of the Internet of Vehicles. In China, China Mobile, China Unicom and China Telecom are the main providers. (7) Government The government is the supervisor and guide in the car networking industry chain, and is also the user of the car networking service, which has a leading and promoting role in this industry. Through the analysis of the vehicle network industry chain, TSP is at the core of the entire industry chain, integrating and supervising the service content, providing services to users in the future, and classifying according to the status of TSP services provided by market participants. The following development models. 3.1 The automaker is in a dominant position OEMs do their own TSP services or control other TSP service providers. The automaker has more profitable items in the car networking industry chain: In addition to the fees paid by the user for purchasing the terminal equipment and ordering the package service, the OEM can obtain a certain profit share by cooperating with the third party; Advertise the advertising revenue of the new media platform for the preferences and needs of the catering, entertainment and leisure venues involved in the travel of the owner; Revenues from the sharing of points of interest, the life service hotspot platform of interest points rankings, and the introduction of hotspot CP/SP resources. Whether it is self-operated TSP or other TSP suppliers to provide services, the OEM has the highest revenue share due to its dominant position and large initial investment. However, throughout the entire Internet of Vehicles market, there is no TSP service that is dominated by OEMs. profit. According to the current situation of China's car networking market, the development model dominated by OEMs is divided into three types: self-operated, joint venture, and pure outsourcing. (1) Self-employed The automaker builds a car networking service brand and provides services by its subsidiaries or departments. Represented by Dongfeng Nissan, its Dongfeng Nissan Data Marketing Company provides the TSP service of CARWINGS. Because it is self-operated, the automaker has complete control rights, high internal communication efficiency, timely problem solving, and timely response to user feedback. At the same time, automakers also face some difficulties in self-employment: The OEM lacks the experience of building and following the operation of the vehicle networking service, and the cost of control is high; Secondly, the initial investment is huge, such as the establishment of T platform, call center, the establishment of specialized companies or departments, the cost is high; The management or operation of the company or department of the automaker has low profit requirements, low pressure and lack of long-term development driving force. (2) Joint venture The OEM and the TSP professional service provider set up a joint venture to jointly operate the car network service of the brand vehicles of the OEM. As the representative of Anjixing, OnStar and SAIC Group each accounted for 40%, and SAIC GM held 20% of the shares. Shanghai Anjixing Company was established to provide security-based car networking services for GM's Cadillac and Chevrolet. In the joint venture model, the vehicle management and professional TSP suppliers have public management operations, which can share resources, experience, talents, etc., and have obvious advantages. However, as a subsidiary of the automaker holding company, the operation has greater independence, mainly focusing on profitability, which may affect the overall vehicle networking strategy of the automaker. Moreover, cooperation between two parties or parties may result in conflicts of interest and internal consumption. (3) pure outsourcing The OEM has signed an outsourcing agreement with the TSP professional service provider, and the outsourced TSP service provider provides the vehicle networking service for the OEM, and the Toyota G-book is outsourced to the 95190. The advantage of this model is that the OEM can manage and control the TSP, lead the business direction, and ensure the efficient operation of the TSP service. After all, the third-party TSP has professional team, operation management experience and a full set of operational qualifications and soundness. Management process. However, there are also problems. The third-party TSP not only serves an OEM, but also has a data leakage risk for the OEM. And once the OEM wants to operate the car networking business itself, the replacement cost is high. 3.2 Communication operators are in a dominant position The business model in which the communications operators are dominant is mainly in the aftermarket. Communication operators develop their own systems for car networking services, including the construction of TSP service operation platforms, planning service functions, procurement and distribution of content, development of sales strategies, pricing and charging, and other activities related to operations. All revenues are distributed by the communication operators based on the cost and the profit contribution rate of each participant. The communication operators have the largest investment and the highest share of revenue. The Smart Screen Protector Cutting Machine can help stores reduce the inventory of Screen Protectors. It is mainly used to cut Screen Protectors such as Mobile Phone Screen Protectors, Watch Screen Protectors, Tablet Screen Protectors, Pad Screen Protectors, and personalized fashion Back Films. It is very suitable for personal business or shop drainage. Screen Protector Cutting Machine,Protective Film Cutting Machine,Back Sticker Cutting Machine,Phone Sticker Cutting Machine, Film Cutting Machine Shenzhen Jianjiantong Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.jjttpucuttingplotter.com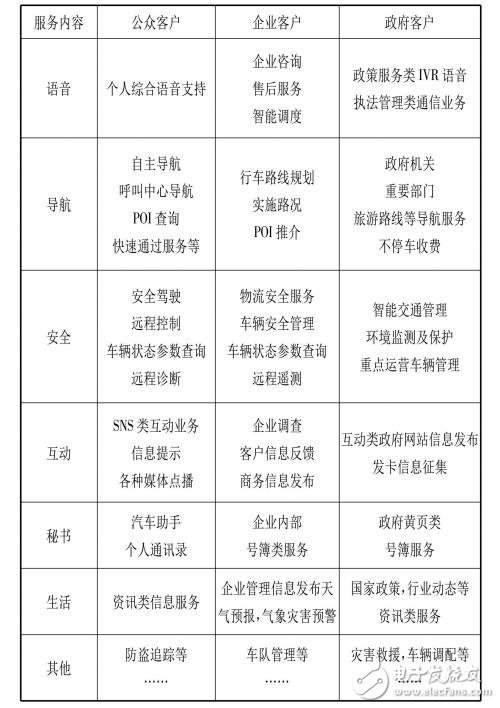
Universal Screen Protector Cutting Machine has 20000+ cloud data of different specifications and models, adopts massive cloud database, and all data is updated synchronously in the state of networking. You'll have a full range of screen protector models on one machine and cut any Screen Protector model as needed without having to stock up on Screen Protectors for various phone models. No more losing customers due to missing models.