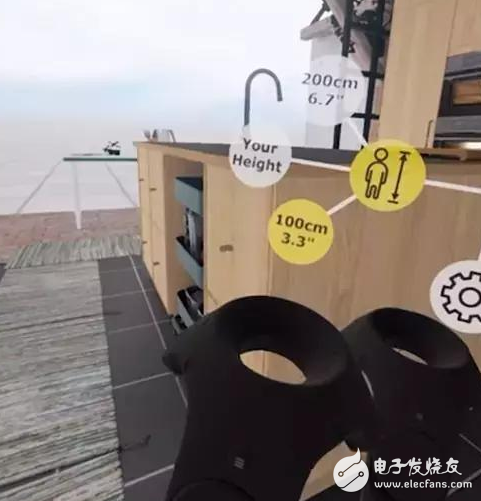
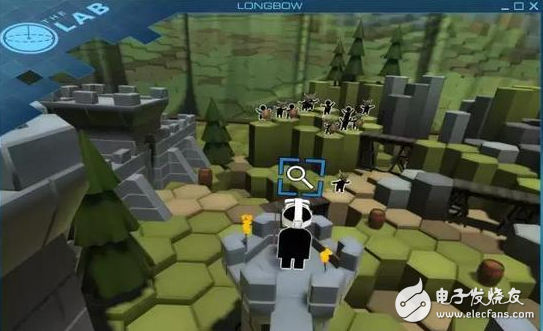
Recently, I (the original author of the English language) started a ten-week centralized training in VR design. During this period, the most exciting thing for me was to evolve and reshape the technical skills I have learned in animation design work over the past few years, and rethink the design process to adapt to new areas. In the second lesson, we practiced in small groups, the task of porting the traditional real-time strategy game mode (Imperial Age, Warcraft, etc.) to the VR experience environment provided by HTC Vive. The idea time was only twenty minutes. I tried to draw a storyboard sketch on 16x9 grid paper, and then quickly realized that VR-oriented design is another level compared to the work areas that I know day after day. Things. For the interface design of the physical screen, we are accustomed to thinking from the perspective of two-dimensional appearance and operational experience. In the VR project, you need to consider human-computer interaction, visual presentation, sound design and so on for the three-dimensional scene. Elements, as a game designer does, have insights into the psychological and behavioral patterns of users in an immersive environment. I need to expand my design mindset, from traditional interface design to spatial perception, sound, touch, ergonomics and so on. To be honest, in just 20 minutes, I can't even find a way to start with these new concepts. But undoubtedly, such a challenging practical course can really open your eyes and learn a lot. Twenty minutes is about to pass, and my other team members finally have some ideas: Just like the literal meaning of the word "God's perspective", the character's character stands on a huge tablet, floating above the clouds and interacting with the world below. The player has a magical tactical belt with tools for commanding operations, including telescopes to view local details of the battlefield, flashlights used to guide soldiers, and more. However, when we did the concept demonstration, we were told by the instructor that some of the ideas were theoretically good, but they were not practical in the VR world. For example, the so-called "belt" only obscures the view of the player when looking down. It is more feasible to replace the concept of "backpack" and let the player select the tool by taking action across the shoulder. In the recent HCD (Human Centered Design) VR design advanced course, the most important thing I learned is to always remember that people are recognized in the virtual world due to many factors. Behavioral capabilities and corresponding experiences can be very different, and the complexity of the situation often exceeds the expectations of product design developers. Combined with the feelings of practical training, I have summarized the six most important aspects of VR design, including a number of points that need to be considered and analyzed, and I will share it with you. The understanding of limitations is the most important, because this will determine the human-computer interaction mode and experience form of a product at a fundamental level. User side limitations How is the target audience of the product defined? Which type of device are they users of? What characteristics might it have? If you want to maximize coverage to more users, mobile VR mode (Daydream, Gear VR, Cardboard) will be more suitable than high-end devices such as Vive and Rift. Remember that VR product experience design needs to focus more on the overall athletic ability of the body than on the eyes and hands. For example, for users who are old or have limited mobility, try to minimize the need for physical involvement, and make necessary restrictions on the duration of interaction to avoid fatigue. For targets that are subject to many young players, this The limitations of the aspect will be very loose, and more and faster sports experience is what these users are pursuing. Hardware limitations What are the technical limitations of the device platform that the product focuses on? To fully understand this point in the early stage, to guide the design of the experience mode, such as whether you need to rely on the handheld controller, whether you need room scale tracking, whether you need high-end PC device support, etc., to avoid the actual development process. Found that some concepts could not be achieved. Limitations of graphics technology What are the limitations of current mainstream game engines? How will these limitations affect your product style? Imagine that you spent a few days creating a styleframe in C4D, but found that you can't be imported into a specific game engine. Limitations of the use environment What are the limitations of the conventional use environment on a spatial scale? Limitations in this area will actually affect the way the virtual world is designed. In what kind of place do users usually wear your head to experience your product? A stable, controlled environment, or on a travel bus or airplane? The product is oriented to a large and open environment such as a pavilion, or is it a small space like a bedroom or an office? What is the specification of the virtual world? Boundless or closed space? How to effectively utilize the hardware capabilities of the equipment that the product focuses on? What is the specification of the protagonist and the proportion in the environment? This will have a significant impact on the user's psychological experience in the virtual world, and for some people it may even trigger claustrophobia or phobia. IKEA's VR app allows users to choose different heights to experience the height ratio of the furniture. What is the distance between the protagonist and the interactive object? In the virtual world, distances of more than 20 meters will make it difficult for users to maintain 3D depth perception. Conversely, due to the limited depth of field of the hardware, objects within 0.5 meters will also be difficult to be clearly focused. If the product provides a room-scale experience, how should you use the boundaries of the room itself? For example, in the game "Longbow", the environment in which the protagonist is located is set as the tower of the castle. The virtual wall is unified with the wall of the room. The limitation of space becomes part of the game environment, not by Some are represented by a borderline that emerges from the air. Very smart solution. Communication Cable,Screen Communication Cable,Pair Cable,Intrinsic Safety Cable Baosheng Science&Technology Innovation Co.,Ltd , https://www.bscables.com